How To Keep Your Eye Lens Flexible
Lens of the center
- What is the lens of the middle?
- Function of the lens of the centre
- Accommodation
- Presbyopia
- Clouding of the lens (cataract)
- When to come across an eye doctor
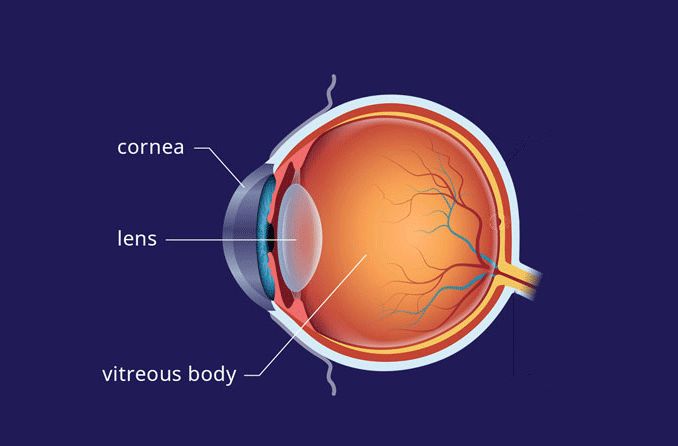
What is the lens of the center?
The lens of the eye, besides called the crystalline lens, is an important part of the eye'south anatomy that allows the center to focus on objects at varying distances. It is located behind the iris and in forepart of the vitreous body.
In its natural land, the lens looks like an elongated sphere — a shape known as ellipsoid — that resembles a deflated brawl. The average lens size in adults is approximately 10 mm across and 4 mm from front to back.
The lens is fabricated up almost entirely of proteins. In fact, proteins brand up about 60% of the eye's lens — a higher protein concentration than whatsoever other bodily tissue. The tissue is transparent, which allows light to easily enter the eye. Information technology's besides flexible, so it can modify shape and bend the calorie-free to focus properly on the retina.
Function of the lens of the eye
The master function of the lens is to bend and focus calorie-free to create a abrupt image. To do that, the lens uses the help of ciliary muscles to stretch and thin out when focusing on distant objects, or to shrink and thicken when focusing on virtually objects.
When light enters the centre, the lens will bend and focus incoming light directly on the retina, which is how the clearest possible image is produced.

The crystalline lens projects a focused prototype on the retina. However, the initial image projected is inverted (either upside downwards or reversed). When the epitome is sent to the brain via the optic nervus, the brain will flip the image dorsum to normal.
The ciliary body is critical for the lens to part correctly. While the ciliary muscles permit the lens to change shape to focus, the lens itself is kept in place past little fibers that are connected to the ciliary torso — these are chosen zonular fibers, or zonules. The ciliary body as well produces aqueous humor, which keeps the lens healthy and functioning.
The lens relies on the aqueous humour for free energy and cleansing rather than nerves or blood menses. Aqueous humor is the clear fluid located between the cornea and the lens that flows through the eye and so drains from the eye through the trabecular meshwork.
Adaptation
Accommodation refers to the lenses' ability to bounce between focusing on about objects and far objects with petty interference.
For example, if you're approaching a traffic light while driving, the lenses in your eyes volition be focused distantly, because the light is relatively far away. As you become closer to the low-cal, your lenses will make tiny changes in shape to arrange the budgeted object that used to exist distant.
Accommodation relies on elasticity of the crystalline lens, which makes it easier to change focal distances. As we age, the crystalline lens loses its elasticity, which results in a condition called presbyopia.
Presbyopia
Presbyopia is a natural, age-related vision change that affects a person's ability to focus on close-upward objects. The status affects well-nigh everyone, fifty-fifty if they've never had vision problems earlier.
The cause of presbyopia is related to alterations inside the lenses' composition. Aging triggers a change in the protein of the lenses, which causes them to thicken and become inflexible. The ciliary muscle fibers that keep the lens in identify and help information technology modify shape are also affected.
All of these developments make it difficult for the optics to focus on nearby objects.
Signs of presbyopia typically begin around the age of forty and gradually progress until historic period 65 or lxx, when presbyopia plateaus. Presbyopia is not harmful and can be corrected with spectacles, contacts or vision surgery.
Clouding of the lens (cataract)
Cataracts occur when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy or hazy, resulting in blurred vision. Advanced age is the leading cause of cataract development, though it's possible for children to be built-in with congenital cataracts.
As the eye ages, the proteins that make upwardly the lens brainstorm to clump together. This may occur in one or both optics and probable will non affect vision in the beginning. Over time, eyesight can appear blurry, dull, hazy or dim, which can greatly impact one'southward power to see in low-light atmospheric condition (at night). If untreated, cataracts can lead to vision loss.
Cataract surgery can be performed to remove the overcast lens and replace it with an bogus one, known every bit an intraocular lens (IOL). There are many types of IOLs available for the surgery, including monofocal, multifocal and toric.
When to see an eye dr.
The lens is a vital part of the middle and makes clear vision possible. Because information technology'south an internal structure, information technology tin can exist difficult to know if something is awry with the lens.
Having an eye doctor conduct a comprehensive eye test gives them the opportunity to look within the middle and make sure everything in it — including the lens — is good for you.
If you notice whatever sudden changes in your vision, or if it'due south been longer than two years since your last eye exam, it'southward time to schedule one. It'due south a small only important pace in keeping your vision clear and your eyes healthy.
RELATED READING: Refractive lens substitution (replacing the natural lenses to correct a refractive error rather than to treat cataracts)
Folio published in February 2021
Page updated in November 2021
Source: https://www.allaboutvision.com/eye-care/eye-anatomy/lens-of-eye/
Posted by: wiggspasuch1942.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Keep Your Eye Lens Flexible"
Post a Comment